PIC/S六月更新文件
2018年6月20日,PIC/S官网发布系列修订文件,包括新修订的GMP以及四篇指导文件。
新发布的GMP主要对第三章“厂房与设施”、第五章“生产”、第八章“投诉与产品召回”以及关于“实时放行测试及参数放行”的附件17进行了修订。修订后的PIC/S GMP指南第三章、第五章、第八章与欧盟GMP指南的相应内容基本一致,仅在语言表达方面略有不同。
另外更新的四篇指导文件分别是关于共用设施交叉污染的PIC/S备忘录(PI 043-1)、关于确定用于人用药所用辅料的GMP水平确定用正式风险评估指南(PI 045-1)、关于设定基于健康的暴露限值的指南,用于在共用设施中制造不同药品的风险识别(PI 046-1)、关于人用药物有效成分良好分配规范原则的指南(PI 047-1)。
目前这些文件均在陆续翻译中。以下为关于确定用于人用药所用辅料的GMP水平确定用正式风险评估指南(PI 045-1)中英对照文件。
GUIDELINES ON THE FORMALISED RISK ASSESSMENT FOR ASCERTAINING THE APPROPRIATE GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICE FOR EXCIPIENTS OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE
人用药所用辅料的GMP水平确定用正式风险评估指南
TABLE OF CONTENTS
目录
Section 1. Document history
文件记录
Section 2. Introduction
介绍
Section 3. Scope
范围
Section 4. Determination of appropriate GMP based on type and use of excipient
基于辅料类型和用途的适当的GMP决策
Section 5. Determinationof excipient manufacturer’s risk profile
确定辅料生产的风险概况
Section 6. Confirmation of application of appropriate GMP
适当GMP申请确认
Section 7. Revision History
修订记录
1. DOCUMENT HISTORY 文件记录
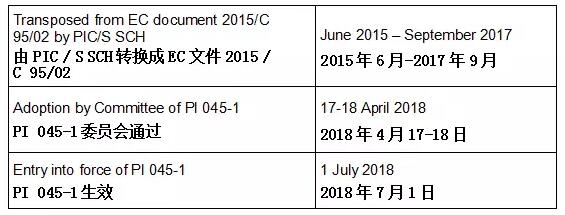
2. INTRODUCTION 介绍
The present PIC/S Guidelines are based on EC document 2015/C 95/02, which has been drafted by the EMA GMDP IWG and transposed for PIC/S purpose by the PIC/S Sub-Committee on the Harmonisation of GM(D)P.
本PIC / S指南是基于EC文件2015 / C 95/02,由EMA GMDP IWG起草、由PIC / S小组委员会协调GM(D)P的PIC/S用途。
These guidelines have been adopted by PIC/S as a guidance document. It is up to each PIC/S Participating Authority to decide whether it should become a legally- binding standard.
这些准则已被PIC / S作为指导性文件。由每个PIC / S参与机构决定是否应成为具有法律约束力的标准。
The manufacturing authorisation holder is required to ensure that the excipients are suitable for use in medicinal products by ascertaining what the appropriate good manufacturing practice (GMP) is. The appropriate GMP for excipients of medicinal products for human use shall be ascertained on the basis of a formalised risk assessment in accordance with these guidelines. The risk assessment shall take into account requirements under other appropriate quality systems as well as the source and intended use of the excipients and previous instances of quality defects. The manufacturing authorisation holder shall ensure that the appropriate GMP ascertained is applied. The manufacturing authorisation holder shall document the measures taken.
生产许可持有人应通过确认适当的GMP保证辅料适用于在药品中的用途。人药用药辅料适当的GMP应根据这些指南,基于正式的风险评估进行确定。风险评估应考虑其他适当质量体系的要求,以及辅料的来源和用途,以及之前的质量缺陷情况。 生产许可持有人应保证所确定的GMP是适用的。生产许可持有人应记录所采取的措施。
The excipient risk assessment/risk management procedure should be incorporated in the pharmaceutical quality system of the manufacturing authorisation holder.
辅料风险评估/风险管理程序应结合生产许可持有人的药品质量体系中。
Manufacturing authorisation holders should have the risk assessment/management documentation for appropriate GMP for excipients available on site for review by GMP inspectors. Consideration should be given to sharing relevant information from the risk assessment with the excipient manufacturer to facilitate continuous improvement.
生产许可持有人应针对辅料所用的适当的GMP要求的风险评估/管理文件记录,并能提供给GMP检查员检查。 应考虑与辅料生产商共享风险评估所产生的相关信息,以促进持续改进。
A risk assessment as set out in these guidelines should be carried out for excipients for authorised medicinal products for human use in accordance with provisions established by applicable national competent authorities.
根据国家有关主管部门的规定,应对人用药品中辅料就这些列出的指南进行风险评估。
3. SCOPE 范围
3.1These guidelines apply to the risk assessment for ascertaining the appropriate GMP for excipients for medicinal products for human use. An excipient is any constituent of a medicinal product other than the active substance and the packaging material.
这些指南适用于风险评估,来评价应用适当的GMP于人用药所用辅料管理。 辅料是药品中不包括活性成分和包装材料在内的其它组成部分。
3.2 These guidelines do not cover substances added to stabilise active substances that cannot exist on their own.
这些指南不涵盖添加入药品中那些不能单独存在、而需要在活性物资中添加稳定剂使活性物质稳定的成分。
4. DETERMINATION OF APPROPRIATE
GMP BASED ON TYPE AND USE OF
EXCIPIENT
基于辅料类型和用途的适当的GMP决策
4.1 In PIC/S PE 009 Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products Annex 20, principles and examples of tools for quality risk management that can be applied to different aspects of pharmaceutical quality, including excipients, can be found.
在PIC / S PE 009 GMP指南附录20中,可以找到能应用于药品质量,包括辅料,不同方面的质量风险管理原则和工具实例。
4.2 These quality risk management principles should be used to assess the risks presented to the quality, safety and function of each excipient and to classify the excipient in question,e.g. as low risk,medium risk or higt risk.Quality risk management tools such as those listed in Annex 20(e.g. hazard analysisand critical controlpoints-HACCP)should be used for this purpose.
这些质量风险管理原则应用于评估每种辅料所呈现的质量、安全和功能方面的风险,并对所述辅料风险等级进行分类,如低风险、中等风险或高风险。 质量风险管理工具,如附件20中列出的《风险分析和关键控制点—HACCP》应用于此目的。
4.3 For each excipient from each manufacturer used, the manufacturing authorisation holder should identify the risks presented to the quality, safety and function of each excipient from its source — be that animal, mineral, vegetable, synthetic, etc. — through to its incorporation in the finished pharmaceutical dose form. Areas for consideration should include, but are not limited to:
来自于每个生厂商的每种辅料,生产许可持有人应从其来源—动物、矿物、植物、合成物等—识别每种辅料的质量、安全和功能风险,直至其最终形成制剂成品。 要考虑的内容应包括但不限于:
(a) transmissible spongiform encephalopathy;
TSE风险
(b) potential for viral contamination;
病毒污染的可能性
(c) potential for microbiological or endotoxin/pyrogen contamination;
微生物或内毒素/热源污染的可能性
(d) potential, in general, for any impurity originating from the raw materials, e.g. aflatoxins or pesticides, or generated as part of the process and carried over, e.g. residual solvents and catalysts;
原料中产生的任何杂质存在的可能性,例如,黄曲霉素或杀虫剂,或工艺生产中产生或带入的杂质,例如,残留溶剂和催化剂。
(e) sterility assurance for excipients claimed to be sterile;
无菌保证用于证明辅料的无菌性
(f) potential for any impurities carried over from other processes, in absence of dedicated equipment and/or facilities;
非专用设备/或设施中其他工艺带入杂质的可能性
(g) environmental control and storage/transportation conditions including cold chain management, if appropriate;
环境控制和存贮运输条件,适当时包括冷链管理
(h) supply chain complexity;
供应链复杂程度
(i) stability of excipient;
辅料的稳定性
(j) packaging integrity evidence.
包装完整性证据
4.4 Additionally, with respect to the use and function of each excipient, the manufacturing authorisation holder should consider:
此外,关于每种辅料的使用和功能方面,生产许可持有人应考虑:
(a) the pharmaceutical form and use of the medicinal product containing the excipient;
含有辅料的药品剂型和药品的用途
(b) the function of the excipient in the formulation, e.g. lubricant in a tablet product or preservative material in a liquid formulation, etc.;
辅料在制剂中的功能,例如,片剂中的润滑剂、液体制剂中的防腐剂等。
(c) the proportion of the excipient in the medicinal product composition;
辅料在药品成分中所占的比例
(d) daily patient intake of the excipient;
患者的日摄入辅料量
(e) any known quality defects/fraudulent adulterations, both globally and at a local company level related to the excipient;
全球范围或当地公司范围与辅料有关的已知的质量缺陷或造假情况
(f) whether the excipient is a composite;
辅料是否是一种成分
(g) known or potential impact on the critical quality attributes of the medicinal product;
对药品关键质量属性的已知的或潜在的影响
(h) other factors as identified or known to be relevant to assuring patient safety.
已识别的或已知的与保证患者安全相关的其他因素
4.5Having established and documented the risk profile of the excipient, the manufacturing authorisation holder should establish and document the elements of the PIC/S PE 009 Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products that he/she believes are needed to be in place in order to control and maintain the quality of the excipient, e.g. Annex 1 or/and Annex 2; Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products Part II: Basic Requirements for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.
在建立或记录辅料的风险概况之后,生产许可持有人应建立和记录PIC/S PE 009 GMP的要素,这些要素应是认为其为控制和维护辅料质量所必须的,例如附录1和/或附录2,GMP第二部分用作起始物料的活性物质的基本要求。
4.6 These elements will vary depending on the source, the supply chain and the subsequent use of the excipient but as a minimum the following higt level GMP elements should be consideredd by the manufacturing authorisation holder;
这些要素会根据辅料的来源、供应链和随后的使用而不同,但生产许可持有人至少应考虑以下水平的GMP要素:
(a) establishment and implementation of an effective pharmaceutical quality system;
建立和实施有效的药品质量体系
(b) sufficient competent and appropriately qualified personnel;
具备足够胜任力与资质合适的人员
(c) defined job descriptions for managerial and supervisory staff responsible for manufacturing and quality activities;
确定对生产和质量活动管理和主管人员的岗位职责
(d) training programmes for all staff involved in manufacturing and quality activities (included but not limited to cleaning, engineering, laboratory, maintenance, materials management, safety, and technical services);
所涉及生产和质量活动的员工的培训项目(包括但不仅限于清洁、工程、实验室、维护、材料管理、安全和技术服务)
(e) training programmes related to health, hygiene and clothing as identified as necessary to the intended operations;
与健康、卫生和服装相关的培训项目,并对其预估操作是必要的;
(f) provision and maintenance of premises and equipment appropriate to the intended operations;
设施和设备的结构和维护适合于其既定操作
(g) documentation system(s) covering all processes and specifications for the various manufacturing and quality operations;
文件记录体系覆盖所有不同生产和质量操作的加工和质量标准
(h) systems for coding and identifying starting materials, intermediates and excipients to allow full traceability;
起始物料、中间体、辅料的编码和识别系统可以进行全程追踪
(i) qualification program of suppliers;
供应商确认程序
(j) system for quality control of the excipient and a responsible person independent from production to release th batches;
对辅料进行系统的质量控制,有一个责任人独立于生产以外来放行批次
(k) retention of records for incoming materials and excipients and retention of samples of excipients for the periods required by PIC/S Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products, Part II;
进场物料和辅料记录应保存,辅料留样时间应符合PIC/S GMP第二部分要求
(l) systems to ensure that any activity contracted out is subject to a written contract;
系统保证所有外包活动都有书面合同
(m) maintenance of an effective system whereby complaints are reviewed and excipients may be recalled;
有效系统的维护、客户投诉进行审核,辅料可能被召回
(n) change management and deviation management system;
变更管理和偏差管理系统
(o) self-inspection program;
自检程序
(p) environmental control and storage conditions.
环境控制和存贮条件
5. DETERMINATION OF EXCIPIENT MANUFACTURER’S RISK PROFILE
确定辅料生产的风险概况
5.1 After determination of the appropriate GMP, a gap analysis of the required GMP against the activities and capabilities of the excipient manufacturer should be performed.
在确定了适当的GMP后,应针对辅料生产商的活动和能力进行所要求的GMP差距分析
5.2 Data/evidence to support the gap analysis should be obtained through audit or from information received from the excipient manufacturer.
用以支持差距分析的数据/证据应通过审计获得,或从辅料生产商处获得的信息。
5.3 Certification of quality systems and/or GMP held by the excipient manufacturer and the standards against which these have been granted should be considered as such certification may fulfill the requirements, subject to national legislation requirements.
质量体系的证书/或辅料生产商持有的GMP证书,和颁布证书所依据的标准应进行考虑,因为该认证可能会满足这些要求,这些要求受国家立法要求的限制。
5.4 Any gaps identified between the required GMP and the activities and capabilities of the excipient manufacturer should be documented.
所识别出的GMP要求与辅料生产商的活动及能力之间的差距应进行记录。
Furthermore, the manufacturing authorisation holder should perform a further risk assessment to determine the risk profile, e.g. low risk, medium risk or high risk, for that excipient manufacturer. PIC/S PE 009 Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products Annex 20: Quality Risk Management should be used for that purpose. Quality risk management tools such as those listed there — HACCP etc. —should be used for this.
另外,生产许可持有人应实施进一步风险评估,以决定该辅料生产商的风险概况,例如,低风险、中等风险或高风险。PIC/S PE 009 GMP指南附件20:质量风险管理工具,例如列于其中的那些---HACCP—等一一应用于此。
5.5 The manufacturing authorisation holder should have a series of strategies ranging from acceptance through control to unacceptable for the different risk profiles and based on these a control strategy, e.g. audit, document retrieval and testing, should be established.
生产许可持有人应制定一系列的策略,对于不同的风险概况从可接受到不可接受,基于这些,应建立一种控制策略,例如,审计、文件恢复和检测。
6. CONFIRMATION OF APPLICATION OF APPROPRIATE GMP
适当的GMP申请确认
6.1 Once the appropriate GMP for the excipient and the risk profile of the excipient manufacturer have been defined, ongoing risk review should be performed through mechanisms such as:
一旦定义了辅料适用的GMP,以及辅料生产商的风险概况,后续通过一定机制进行持续风险评估,如:
(a) numberof defects connected to batches of excipient received;
与收到的辅料批次相关的缺陷数量
(b) type/severity of such defects;
这些缺陷的类型和严重程度
(c) monitoring and trend analysis of excipient quality;
辅料质量的监控和趋势分析
(d) loss of relevant quality system and/or GMP certification by excipient manufacturer;
相关质量体系的缺失和/或辅料生产商持有的GMP证书
(d) observation of trends in drug product quality attributes;this will depend on the nature and role of excipient;
药品质量属性的趋势观察,这些将取决于辅料的属性和作用
(e) observed organisational, procedural or technical/process changes at the excipient manufacturer;
观察到的辅料生产商的有组织性的、程序性的或技术性的/工艺变更
(f) audit/re-audit of excipient manufacturer;
对辅料生产商进行审计/复审
(g) questionnaires.
问卷
Based on the outcome of the risk review, the established control strategy should be reviewed and revised if needed.
基于风险审核的结果,必要时应对已建立的控制策略进行审核与修订












